4.4 Solidification
A message is solid if all its parents are stored, solid and valid. This section defines how messages get solid in the Tangle.
The Solidification specification depends on the following specifications:
4.4.1 Motivation
Solidification is a process of requesting missing referenced messages. It may be recursively repeated until all of a message's past cone up to the genesis (or snapshot) becomes solid.
In that way, the Tangle enables all nodes to retrieve all of a message's history, even the ones joining the network at a point later in time.
4.4.2 Definitions
valid: A message validity status is initialized as valid, and it's set as invalid whenever the message does not pass any of the filters from the solidifier and from the message booker:
Solidifier: checks if parents are valid,
- Booker: checks if the contained transaction is valid. Note that only messages containing a transaction are required to perform this check, which are defined in Section 5.1 - UTXO
parents age check: A check that ensures the timestamps of parents and child are valid, following the details defined in Section 4.2 - Timestamps.
solid: A message is solid if it passes the solidification check and all its parents are stored in the storage, solid and their validity status is set as valid.
4.4.3 Parameters
retryInterval: The time interval of resending the same solidification request.maxRequestThreshold: The maximum retry times to send a solidification request.
4.4.4 Solidification and Solidfication Check
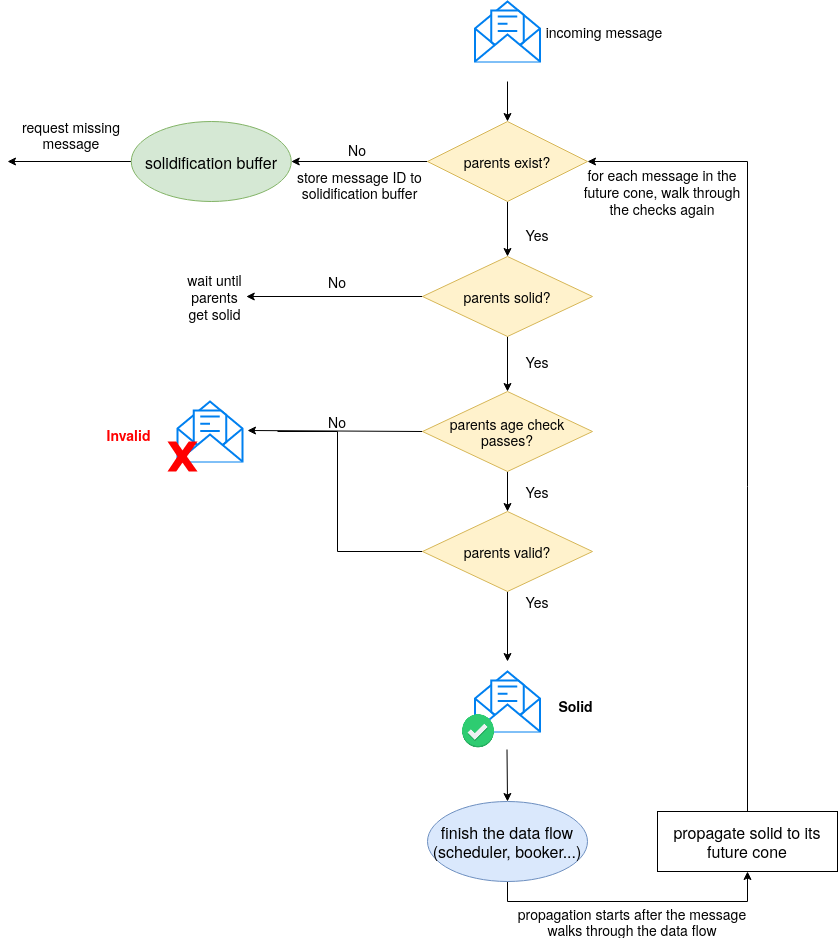
During solidification, if a node is missing a referenced message, the corresponding message ID is stored in the solidification buffer. A node asks its neighbors for the missing message by sending a solidification request containing the message ID.
It also sets a boolean flag isStrongRequest for whether the missing message was requested as a strong (TRUE) or weak (FALSE) parent. This information can be used to decide which checks a message shall pass, when the message is received.
Note that through the following process the parents of a message that is requested through a weak solidification are not requested, and also the message does not have to pass the parent age check.
If a message gets solid, it shall walk through the rest of the data flow, then propagate the solid status to its future cone by performing the solidification checks on each of the message in its future cone again.
Strong Solidification
Once the requested message is received from its neighbors, its message ID shall be removed from the solidification buffer. If isStrongRequest==TRUE the requested message is marked as solid after it passes the strong solidification checks. If any of the checks fails, the message remains unsolid, or is set to invalid, see. Image 4.4.1.
In the strong solidification check we check if
- the parents exist;
- the parents are solid, and if not wait until these get solid;
- the parents age check passes,
- the parents are valid.
Weak Solidification
Once the requested message is received from its neighbors, its message ID shall be removed from the solidification buffer. If isStrongRequest==FALSE the requested message is marked as solid.
No weak solidification check has to be performed.
Image 4.4.1: Strong solidification process.
4.4.5 Communication Details
Nodes send and receive solidification request/response via gossip layer. The solidification request is created and scheduled by the gossip manager, if a node does not get the requested message, the gossip manager re-sends it every retryInterval. If the requested message is not received within maxRequestThreshold rounds, the solidification request must be removed from the solidification buffer.
4.4.5.1 Request and Response
Below we define the form of SolidificationRequest and SolidificationResponse:
SolidificationRequest
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | uint8 | Indicates that the packet is SolidificationRequest. |
| messageID | ByteArray[32] | Contains the message ID of the requested message. |
Table 4.4.2: SolidificationRequest data fields description.
SolidificationResponse
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| type | uint8 | Indicates that the packet is SolidificationResponse. |
| message | ByteArray | Contains the entire requested message. |
Table 4.4.3: SolidificationResponses data fields description.
4.4.6 Denial of Service
All requests/responses exchanged during the solidification are sent via UDP. As such, any UDP based Denial of Service attack may harm the normal functionality of the solidification. To limit this, hardware based protection such as firewall or alternatively may be used.